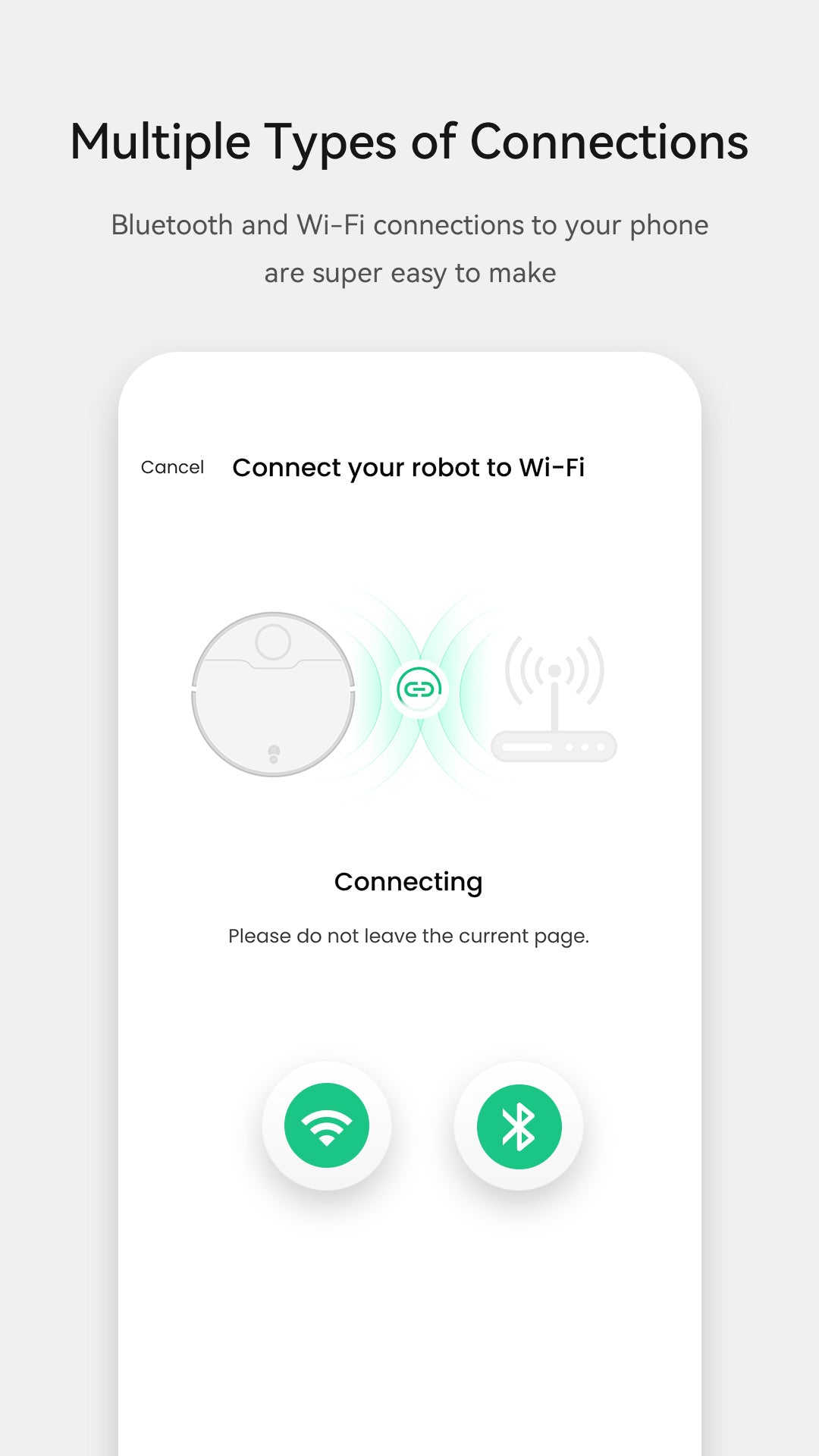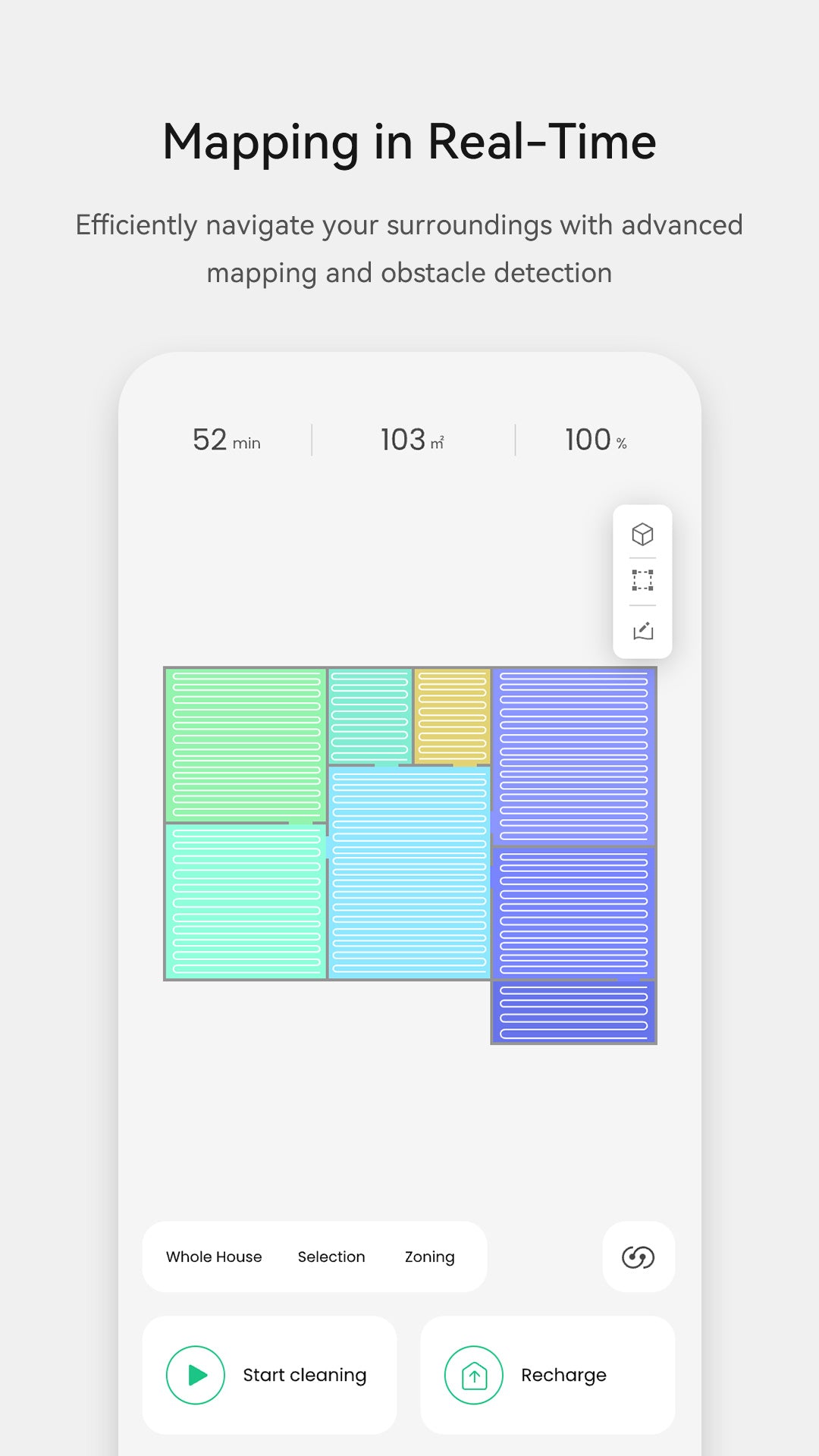
The market for smart home devices has witnessed exponential growth in recent years, with robot vacuum cleaners leading the charge. These innovative appliances not only promise convenience but also integrate advanced technology that requires careful consideration of legal and regulatory frameworks. As a user and observer of this evolving landscape, I find it imperative to explore the implications surrounding robot vacuum cleaner apps.
Understanding the Regulatory Framework Surrounding Robot Vacuum Cleaner Apps
Robot vacuum cleaner apps are designed to enhance user experience by providing features such as remote control, scheduling, and real-time monitoring. However, their integration into our daily lives raises important legal considerations regarding data privacy and consumer protection. The collection of personal data through these applications necessitates compliance with regulations like GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California. Furthermore, governments may offer subsidies and incentives for industries adopting such technologies to promote innovation while ensuring adherence to safety standards.
The Quiet Self-Cleaning Vacuum: A Case Study on Subsidies and Incentives
The quiet self-cleaning vacuum exemplifies how technological advancements can align with government initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable practices. Many jurisdictions provide financial incentives for manufacturers who develop energy-efficient models that reduce noise pollution—a significant concern among consumers living in urban areas. By leveraging these subsidies, companies can invest further in research and development while adhering to environmental regulations that govern product design.
Find more about quiet self cleaning vacuum.
Tuvacs: Navigating Subsidies within Industry Regulations
Tuvacs represents a notable player within the realm of robot vacuums benefiting from industry-specific subsidies aimed at fostering innovation. Their commitment to producing eco-friendly products aligns seamlessly with governmental objectives focused on reducing carbon footprints across various sectors. By taking advantage of available grants or tax breaks tied to sustainability efforts, Tuvacs not only enhances its competitive edge but also contributes positively towards meeting regulatory requirements set forth by environmental agencies.
Conclusion
In summary, robot vacuum cleaner apps embody a complex interplay between technological advancement and legal regulation—particularly concerning data privacy laws as well as industry-specific subsidies aimed at encouraging sustainable practices. As we continue embracing automation within our homes, understanding these dynamics will be crucial for both consumers seeking efficient solutions and manufacturers striving for compliance amidst an ever-evolving regulatory environment.